The Bloch sphere
Unitary operations on a single qubit form a group.
More precisely, the set of all (2\times 2) unitary matrices forms a (non-abelian) group under matrix multiplication, denoted by \mathrm{U}(2).
It turns out that compositions of single-qubit unitaries behave pretty much the same as compositions of rotations in three dimensions.
Technically speaking, we claim that \mathrm{U}(2)/\mathrm{U}(1)\cong \mathrm{SO}(3).
That is, (2\times 2) unitaries, up to global phase, form a group which is isomorphic to the group of rotations in three dimensions, which denoted by \mathrm{SO}(3).
This isomorphism helps to visualise the actions of single-qubit gates.
There are many ways to introduce this isomorphism.
Here we will just show how to represent single-qubit state vectors in terms of Euclidean vectors in three dimensions; later (in Section 3.4) we will actually relate unitary operations on state vectors to rotations in this Euclidean space, demonstrating this isomorphism.
Any single-qubit state can be written as |\psi\rangle=\alpha|0\rangle+\beta|1\rangle, constrained by the relation |\alpha|^2+|\beta|^2=1.
This suggests a more natural parametrisation as
|\psi\rangle =
\cos(\theta/2)e^{i\varphi_0}|0\rangle + \sin(\theta/2)e^{i\varphi_1}|1\rangle
(note that there is a good reason to use \theta/2 instead of \theta, and we we will explain why later on).
We can then factor out a global phase:
|\psi\rangle =
e^{i\varphi_0}\left(
\cos(\theta/2)|0\rangle + \sin(\theta/2)e^{i\varphi}|1\rangle
\right),
and even remove it completely, since states that are identical up to a global phase are physically indistinguishable.
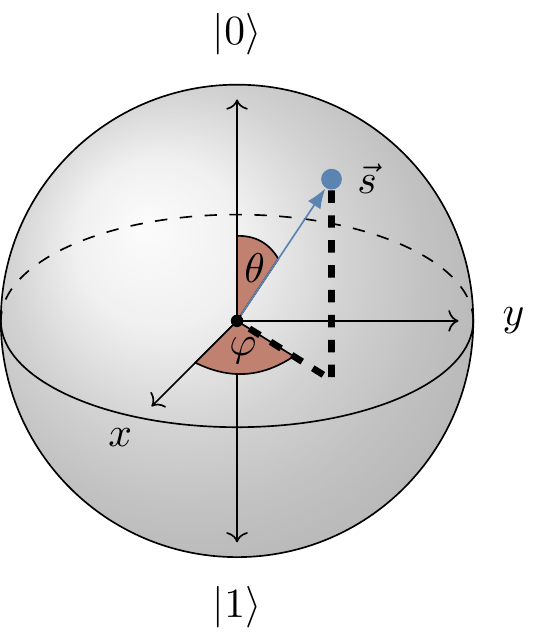
The parametrisation in terms of \theta and \varphi should remind you (if you are familiar with it) of spherical polar coordinates for the surface of a sphere.
We call this sphere the Bloch sphere, and the unit vector \vec{s} defined by \theta and \varphi the Bloch vector.
This is a very useful way to visualise quantum states of a single qubit and unitary operations that we perform on it.
Any unitary action on the state vector will induce a rotation of the corresponding Bloch vector.
But what kind of rotation?
We give a complete answer to this question soon, in Section 3.4, but we might as well give some specific results here first, since some are easy enough to calculate “by hand”.
Here is one fundamental observation: any two orthogonal state vectors appear on the Bloch sphere as two Bloch vectors pointing in opposite directions.
Now, the two eigenvectors of a single-qubit unitary U are always orthogonal, and so must define an axis running through the centre of the Bloch sphere.
This is the axis about which the Bloch vector is rotated when U acts on the corresponding state vector.
The rotation angle \alpha is given by the eigenvalues of U, which, up to a global phase factor, are of the form e^{\mp i\alpha/2}.
It is instructive to work out few simple cases and get a feel for the rotations corresponding to the most common unitaries.
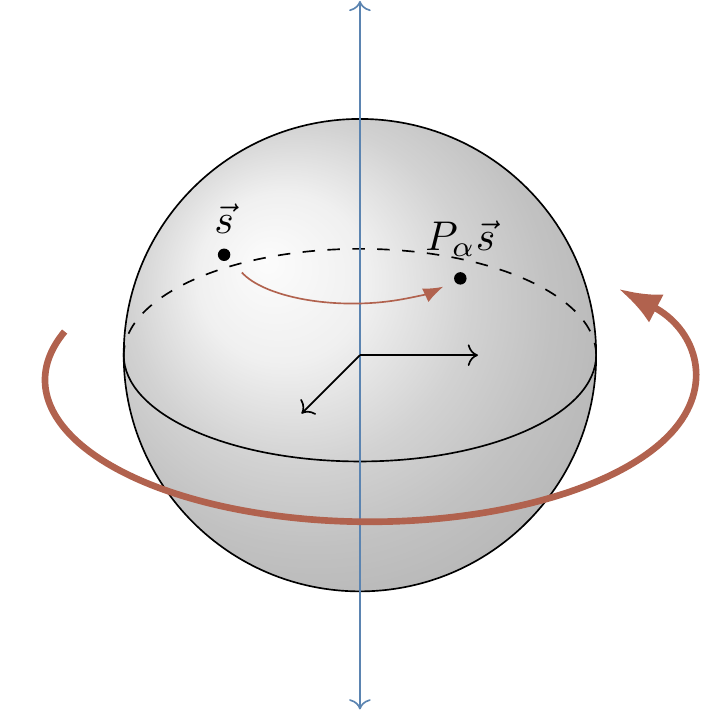
For example, it is easy to check that a phase gate P_\alpha acts by
\cos\frac{\theta}{2}|0\rangle + e^{i\varphi}\sin\frac{\theta}{2}|1\rangle
\longmapsto
\cos\frac{\theta}{2}|0\rangle + e^{i(\varphi+\alpha)}\sin\frac{\theta}{2}|1\rangle.
The azimuthal angle changes from \varphi to \varphi+\alpha, and so the Bloch sphere is rotated anticlockwise by \alpha about the z-axis.
The Bloch vectors corresponding to the two eigenvectors of P_\alpha, namely |0\rangle and |1\rangle, define the axis of the rotation.
As previously mentioned, the Pauli operator Z=\sigma_z is a special case of a phase gate, and represents rotation by {180}^{\circ} (that is, \pi radians), about the z-axis.
You can also verify that X=\sigma_x, with eigenvectors {(|0\rangle\pm|1\rangle)/\sqrt{2}}, represents rotation by {180}^{\circ} about the x-axis, and Y=\sigma_y, with eigenvectors {(|0\rangle\pm i|1\rangle)/\sqrt{2}}, represents rotation by {180}^{\circ} about the y-axis.
Again, note that, by the definition of the axis, the points of intersection of these axes with the Bloch sphere are exactly the eigenvectors of the operator.
How about the Hadamard gate?
Like the Pauli operators, it squares to the identity (H^2=\mathbf{1}), which implies that its eigenvalues are \pm 1.
Thus it will correspond to a rotation by {180}^{\circ}.
But about which axis?
This time, rather than finding eigenvectors of H, we notice that HXH=Z and HZH=X, thus H must swap the x- and z-axes, turning rotations about the z-axis into rotations about the x-axis, and vice versa.
The Hadamard gate must then represent rotation by {180}^{\circ} about the diagonal (x+z)-axis.
You may also notice that, after this rotation, the y-axis points in the opposite direction, which seems to be related to another identity: HYH=-Y.
This is not a coincidence!
We will eventually show that the effect of the rotation represented by unitary U on the Bloch vector with components s_x, s_y, s_z is summarised in the formula
U (s_x X + s_y Y + s_z Z) U^\dagger
= s'_x X+ s'_y Y + s'_z Z,
where s'_x, s'_y, and s'_z are the components of the rotated Bloch vector.